| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Octans |
| Right ascension | 17h 00m 58.51777s[2] |
| Declination | −86° 21′ 51.4707″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.03±0.01[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | subgiant[4] |
| Spectral type | A3 IV[5] |
| U−B color index | +0.02[6] |
| B−V color index | +0.05[6] |
| Variable type | α2 CVn[7] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 7.1±0.5[8] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +8.413 mas/yr[2] Dec.: −0.032 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 5.1828 ± 0.0486 mas[2] |
| Distance | 629 ± 6 ly (193 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.36[9] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.98±0.05[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.64[10] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 111[11] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.45±0.07[12] cgs |
| Temperature | 8,791[13] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.6[14] dex |
| Rotation | ≈2.8 days[13] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 92±6[13] km/s |
| Age | 188±4[4] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
CW Octantis, also known as HD 148542, is a solitary, white hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.03, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 place the object at a distance of 629 light years. It appears to be receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of 7.1 km/s.
CW Octantis has a stellar classification of A3 IV, indicating that it is an evolved A-type star heading towards the red giant branch. Zorec and Royer (2012) model it as a dwarf star that has just reached the end of its main sequence lifetime.[4] It has 2.98 times the mass of the Sun[4] and 4.6 times its radius.[10] It radiates 111 times the luminosity of the Sun[11] from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 8,791 K.[13] CW Octantis is estimated to be 188 million years old.[4]
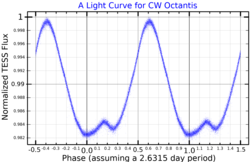
This object is classified as a Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable.[7] Most stars of this class have chemical peculiarities in their spectra, but CW Octantis seems to be ordinary. Renson and Manfroid (2009) consider its peculiarity status to be doubtful.[17] Nevertheless, CW Octantis fluctuates between 6.05 and 6.07 in the Hipparcos passband within 2.63 days.[18] It takes 2.8 days to complete a full a rotation, which corresponds to a projected rotational velocity of 92 km/s.[13]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
MASTwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
GaiaDR3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Tycho2000was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
Zorec2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
de Vaucouleurs1957was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Johnson1966was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Samus2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Gontcharov2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Anderson2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Kervella2021was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
McDonald2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Stassun2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
Reiners2004was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rainer2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Gould1879was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Renson2009was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Watson2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page).