| Cabin Creek | |
|---|---|
 Cabin Creek near Ronda | |
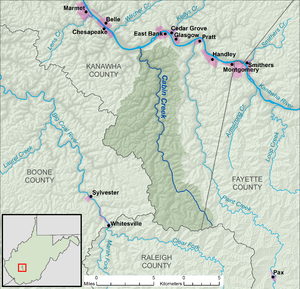 A map of Cabin Creek and its watershed | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | West Virginia |
| Counties | Fayette, Kanawha |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | south-southwest of Coalfield |
| • coordinates | 37°58′25″N 81°21′47″W / 37.9737203°N 81.3631638°W[1] |
| • elevation | 2,311 ft (704 m)[2] |
| Mouth | Kanawha River |
• location | Cabin Creek |
• coordinates | 38°11′56″N 81°28′48″W / 38.1989922°N 81.4801162°W[1] |
• elevation | 591 ft (180 m)[1] |
| Length | 22.7 mi (36.5 km) |
| Basin size | 73 sq mi (190 km2) |
| Basin features | |
| Hydrologic Unit Code | 0505000602 (USGS) |
Cabin Creek is a tributary of the Kanawha River, 22.7 miles (36.5 km) long,[3] in West Virginia in the United States. Via the Kanawha and Ohio rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 72.6 square miles (188 km2)[4] in a coal mining region on the unglaciated portion of the Allegheny Plateau.
Cabin Creek begins in western Fayette County, approximately 2.2 miles (3.5 km) south-southwest of Coalfield. It flows in southern Kanawha County for most of its course, north-northwestward through the unincorporated communities of Republic, Carbon, Decota, Laing, Quarrier, Holly, Leewood, Eskdale, Ohley, Coal, Giles, Dawes, Miami, Sharon, Ronda, and Dry Branch, to the community of Cabin Creek, where it flows into the Kanawha River. The creek is paralleled by county roads for most of its course, and additionally by the West Virginia Turnpike from Giles to its mouth.[5][6]
Cabin Creek was named for a nearby pioneer's cabin which was raided by Native Americans in the 1740s.[7]
- ^ a b c Geographic Names Information System. "Geographic Names Information System entry for Cabin Creek (Feature ID #1536826)". Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ The National Map elevation for GNIS source coordinates. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ United States Environmental Protection Agency. "West Virginia, Upper Kanawha Watershed". Archived from the original on 2013-12-02. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset, area data for Cabin Creek watershed, 10-digit Hydrologic Unit Code 0505000602. The National Map Archived 2012-03-29 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved 2013-11-14
- ^ The National Map Archived 2012-03-29 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 2013-11-15
- ^ West Virginia Atlas & Gazetteer. Yarmouth, Me.: DeLorme. 1997. pp. 52–53. ISBN 0-89933-246-3.
- ^ Kenny, Hamill (1945). West Virginia Place Names: Their Origin and Meaning, Including the Nomenclature of the Streams and Mountains. Piedmont, WV: The Place Name Press. p. 146.