
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cadmium oxide
| |
| Other names
Cadmium(II) oxide,
Cadmium monoxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.770 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2570 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CdO | |
| Molar mass | 128.413 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless powder (alpha form) red-brown crystal (beta form) [1] |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 8.15 g/cm3(crystalline), 6.95 g/cm3 (amorphous)[2] solid. |
| Melting point | 900–1,000 °C (1,650–1,830 °F; 1,170–1,270 K) decomposition of amorphous form[3] |
| Boiling point | 1,559 °C (2,838 °F; 1,832 K) sublimation[3] |
| 4.8 mg/L (18 °C)[4] | |
| Solubility | soluble in dilute acid slowly soluble in ammonium salts insoluble in alkalies |
| Vapor pressure | 0.13 kPa (1000 °C) 2.62 kPa (1200 °C) 61.4 kPa (1500 °C)[5] |
| Band gap | 2.18 eV |
| Electron mobility | 531 cm2/V·s |
| -3.0·10−5 cm3/mol | |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.7 W/m·K |
Refractive index (nD)
|
2.49 |
| Structure | |
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
a = 4.6958 Å
| |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
43.64 J/mol·K[4] |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
55 J/mol·K[6] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−258 kJ/mol[5][6] |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
-229.3 kJ/mol[4] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   [7] [7]
| |
| Danger | |
| H330, H341, H350, H361, H372, H410[7] | |
| P201, P260, P273, P281, P284, P310[7] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
72 mg/kg (oral, rat)[9] 72 mg/kg (oral, mouse)[10] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
500 mg/m3 (rat, 10 min) 2500 mg/m3 (rabbit, 10 min) 3500 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 10 min) 4000 mg/m3 (dog, 10 min) 780 mg/m3 (rat, 10 min) 340 mg/m3 (mouse, 10 min) 3000 mg/m3 (rabbit, 15 min) 3000 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 15 min) 400 mg/m3 (dog, 10 min)[10] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
[1910.1027] TWA 0.005 mg/m3 (as Cd)[8] |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca[8] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [9 mg/m3 (as Cd)][8] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] [dead link] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Cadmium sulfide Cadmium selenide Cadmium telluride |
Other cations
|
Zinc oxide Mercury oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
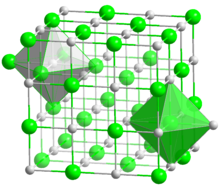
Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers.[11] It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals.[12] Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor[13] with a band gap of 2.18 eV (2.31 eV) at room temperature (298 K).[14]
- ^ Patnaik, Pradyot (2003). Handbook of Inorganic Chemical Compounds. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-049439-8.
- ^ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards". Retrieved 2007-02-16.
- ^ a b "INCHEM: Chemical Safety Information from Intergovernmental Organizations". Retrieved 2007-02-16.
- ^ a b c "Cadmium oxide".
- ^ a b Cadmium oxide in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD) (retrieved 2014-05-23)
- ^ a b Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A21. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Cadmium oxide. Retrieved on 2014-05-23.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0087". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/1306-19-0 [dead link]
- ^ a b "Cadmium compounds (as Cd)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Wells, A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ^ Lewis, Richard J. Sr., Hawley's condensed chemical dictionary, 13th ed., 1997, p. 189
- ^ T. L. Chu; Shirley S. Chu (1990). "Degenerate cadmium oxide films for electronic devices". Journal of Electronic Materials. 19 (9): 1003–1005. Bibcode:1990JEMat..19.1003C. doi:10.1007/BF02652928. S2CID 95361658.
- ^ S. K. Vasheghani Farahani; et al. (2013). "Temperature dependence of the direct bandgap and transport properties of CdO". Applied Physics Letters. 102 (2): 022102. Bibcode:2013ApPhL.102b2102V. doi:10.1063/1.4775691.
