 2D structure of calcium citrate
| |
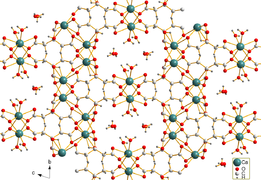 Calcium citrate tetrahydrate[1]
| |
 Calcium citrate tetrahydrate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylic acid calcium salt (2:3)
| |
| Other names
E333, tricalcium dicitrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.265 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E333 (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ca3(C6H5O7)2 | |
| Molar mass | 498.4334 g/mol (anhydrous) 570.4945 g/mol (tetrahydrate) |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.63 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.00 g/cm3 (tetrahydrate)[1] |
| Melting point | Decomposes |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 0.85 g/L (18 °C) 0.95 g/L (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol |
| Structure | |
| Triclinic (tetrahydrate) | |
| P1, No. 2 | |
a = 0.59466(4) nm, b = 1.02247(8) nm, c = 1.66496(13) nm α = 72.213(7)°, β = 79.718(7)°, γ = 89.791(6)°[1]
| |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Magnesium citrate Strontium citrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Calcium citrate is the calcium salt of citric acid. It is commonly used as a food additive (E333), usually as a preservative, but sometimes for flavor. In this sense, it is similar to sodium citrate. Calcium citrate is also found in some dietary calcium supplements (e.g. Citracal or Caltrate). Calcium makes up 24.1% of calcium citrate (anhydrous) and 21.1% of calcium citrate (tetrahydrate) by mass. The tetrahydrate occurs in nature as the mineral Earlandite.
