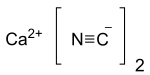
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
calcium dicyanide
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
calcium dicyanide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.856 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ca(CN)2 | |
| Molar mass | 92.1128 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Odor | hydrogen cyanide |
| Density | 1.853 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 640 °C (1,184 °F; 913 K) (decomposes) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, weak acids |
| Structure | |
| rhombohedric | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Highly Toxic |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Non-flammable | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
39 mg/kg rat, oral[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Calcium cyanide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca(CN)2. It is the calcium salt derived from hydrocyanic acid. It is a white solid, although the pure material is rarely encountered. It slowly hydrolyses in solution or moist air to release hydrogen cyanide and is very toxic.[3]
- ^ "GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank". gestis-dguv-de. Retrieved 2022-04-16.
- ^ "CALCIUM CYANIDE | CAMEO Chemicals | NOAA".
- ^ Gail, Ernst; Gos, Stephen; Kulzer, Rupprecht; Lorösch, Jürgen; Rubo, Andreas; Sauer, Manfred (2004). "Cyano Compounds, Inorganic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_159.pub2. ISBN 3527306730.
