 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Foipan |
| Other names | FOY-305 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
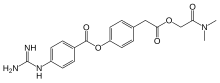
| Formula | C20H22N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 398.419 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Camostat is a serine protease inhibitor. Serine protease enzymes have a variety of functions in the body, and so camostat has a diverse range of uses. Camostat is approved in Japan for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis and postoperative reflux esophagitis.[1][2] The oral proteolytic enzyme inhibitor has been on the market since 1985 under the trade name Foipan Tablets. The manufacturer is Ono Pharmaceutical. The drug is used in the treatment of some forms of cancer and is also effective against some viral infections, as well as inhibiting fibrosis in liver or kidney disease or pancreatitis.[3][4][5][6][7]
- ^ "FOIPAN® Tablets 100mg" (PDF). Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- ^ "Camostat". drugs.com.
- ^ Okuno M, Kojima S, Akita K, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Adachi S, Sano T, et al. (January 2002). "Retinoids in liver fibrosis and cancer". Frontiers in Bioscience. 7 (4): d204–d218. doi:10.2741/A775. PMID 11779708.
- ^ Hsieh HP, Hsu JT (2007). "Strategies of development of antiviral agents directed against influenza virus replication" (PDF). Current Pharmaceutical Design. 13 (34): 3531–3542. doi:10.2174/138161207782794248. PMID 18220789.
- ^ Kitamura K, Tomita K (February 2012). "Proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel and therapeutic application of a serine protease inhibitor for the treatment of salt-sensitive hypertension". Clinical and Experimental Nephrology. 16 (1): 44–48. doi:10.1007/s10157-011-0506-1. PMID 22038264. S2CID 6522071.
- ^ Zhou Y, Vedantham P, Lu K, Agudelo J, Carrion R, Nunneley JW, et al. (April 2015). "Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry". Antiviral Research. 116: 76–84. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.01.011. PMC 4774534. PMID 25666761.
- ^ Ueda M, Uchimura K, Narita Y, Miyasato Y, Mizumoto T, Morinaga J, et al. (2015). "The serine protease inhibitor camostat mesilate attenuates the progression of chronic kidney disease through its antioxidant effects". Nephron. 129 (3): 223–232. doi:10.1159/000375308. PMID 25766432. S2CID 207652863.