| Canine space | |
|---|---|
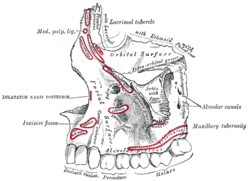 Lateral view of the maxilla, showing infra-orbital area, including the canine fossa, and muscle attachments. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
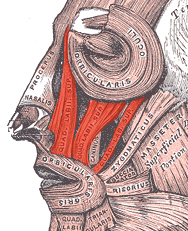
The canine space (also termed the infra-orbital space)[1] is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial spaces or tissue spaces). It is a thin potential space on the face, and is paired on either side. It is located between the levator anguli oris muscle inferiorly and the levator labii superioris muscle superiorly.[1][2] The term is derived from the fact that the space is in the region of the canine fossa, and that infections originating from the maxillary canine tooth may spread to involve the space. Infra-orbital is derived from infra- meaning below and orbit which refers to the eye socket.

- ^ a b Hargreaves KM; Cohen S, eds. (2010). Cohen's pathways of the pulp. Berman LH (web editor) (10th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier. pp. 590–594. ISBN 978-0-323-06489-7.
- ^ Hupp JR, Ellis E, Tucker MR (2008). Contemporary oral and maxillofacial surgery (5th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier. pp. 317–333. ISBN 9780323049030.