| Cape honey bee | |
|---|---|

| |
| A Cape honey bee on a Oxalis pes-caprae flower | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Apidae |
| Genus: | Apis |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | A. m. capensis
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Apis mellifera capensis Eschscholtz, 1822
| |
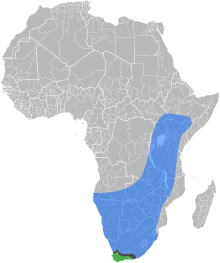
| |
| The natural ranges of the
Cape honey bee,
African honey bee, and the
contact zone where the two subspecies overlap and hybridize
| |
The Cape honey bee or Cape bee (Apis mellifera capensis) is a southern South African subspecies of the western honey bee. They play a major role in South African agriculture and the economy of the Western Cape by pollinating crops and producing honey in the Western Cape region of South Africa. The species is endemic to the Western Cape region of South Africa on the coastal side of the Cape Fold mountain range.
The Cape honey bee is unique among honey bee subspecies because workers can lay diploid, female eggs, by means of thelytoky,[1] while workers of other subspecies (and, in fact, unmated females of virtually all other eusocial insects) can only lay haploid, male eggs. Not all workers are capable of thelytoky – only those expressing the thelytoky phenotype, which is controlled by a recessive allele at a single locus (workers must be homozygous at this locus to be able to reproduce by thelytoky).[2]
The bee tends to be darker in colour than the African honey bee (A.m. scutellata) with an almost entirely black abdomen, this differentiates it from African honey bees which have a yellow band on the upper abdomen. Other differences that might allow for differentiation of the subspecies from African honey bees are their propensity to lay multiple eggs in a single cell and the raised capping on their brood cells.[3]
- ^ Joanna Klein (9 June 2016). "Scientists Find Genes That Let These Bees Reproduce Without Males". The New York Times. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ Lattorff, H.M. G., Mortiz, R.F.A. and Fuchs, S. 2005. A single locus determines thelytokous parthenogenesis of laying honeybee workers (Apis mellifera capensis). Heredity. 94: 533–537.
- ^ "Honeybees of South Africa | SABIO". www.sabio.org.za. Retrieved 2021-09-27.