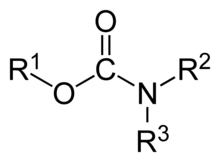
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula R2NC(O)OR and structure >N−C(=O)−O−, which are formally derived from carbamic acid (NH2COOH). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion H2NCOO− (e.g. ammonium carbamate).[1]
Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups −NH−C(=O)−O− are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See § Etymology for clarification.
- ^ Jäger, Peter; Rentzea, Costin N.; Kieczka, Heinz (2000). "Carbamates and Carbamoyl Chlorides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_051. ISBN 3-527-30673-0.