| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
9H-Carbazole[1] | |
| Other names
9-azafluorene
dibenzopyrrole diphenylenimine diphenyleneimide USAF EK-600 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3956 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.542 |
| EC Number |
|
| 102490 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H9N | |
| Molar mass | 167.211 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.301 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 246.3 °C (475.3 °F; 519.5 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 354.69 °C (670.44 °F; 627.84 K)[2] |
| −117.4 × 10−6 cm3 mol−1 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H341, H351, H400, H411, H413 | |
| P201, P202, P273, P281, P308+P313, P391, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
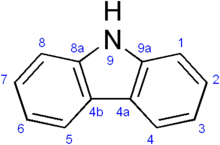
Carbazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound. It has a tricyclic structure, consisting of two six-membered benzene rings fused on either side of a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound's structure is based on the indole structure, but in which a second benzene ring is fused onto the five-membered ring at the 2–3 position of indole (equivalent to the 9a–4a double bond in carbazole, respectively).
Carbazole is a constituent of tobacco smoke.[3]
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 212. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c Lide, David R. (2007). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 88th Edition. CRC Press. pp. 3–86. ISBN 978-0-8493-0488-0.
- ^ Talhout, Reinskje; Schulz, Thomas; Florek, Ewa; Van Benthem, Jan; Wester, Piet; Opperhuizen, Antoon (2011). "Hazardous Compounds in Tobacco Smoke". Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 8 (12): 613–628. doi:10.3390/ijerph8020613. PMC 3084482. PMID 21556207.