| Cardiac marker | |
|---|---|
 | |
| LOINC | 58260-1 |
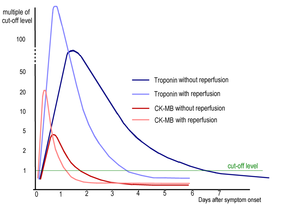
Cardiac markers are biomarkers measured to evaluate heart function. They can be useful in the early prediction or diagnosis of disease.[1] Although they are often discussed in the context of myocardial infarction, other conditions can lead to an elevation in cardiac marker level.[2][3]
Cardiac markers are used for the diagnosis and risk stratification of patients with chest pain and suspected acute coronary syndrome and for management and prognosis in patients with diseases like acute heart failure.
Most of the early markers identified were enzymes, and as a result, the term "cardiac enzymes" is sometimes used. However, not all of the markers currently used are enzymes. For example, in formal usage, troponin would not be listed as a cardiac enzyme.[4]
- ^ Rao SP, Miller S, Rosenbaum R, Lakier JB (2019). "Opportunities for microRNAs in the Crowded Field of Cardiovascular Biomarkers". Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease. 14: 211–238. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012827. PMC 6442682. PMID 30332561.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Rao SP, Miller S, Rosenbaum R, Lakier JB (August 1999). "Cardiac troponin I and cardiac enzymes after electrophysiologic studies, ablations, and defibrillator implantations". Am. J. Cardiol. 84 (4): 470, A9. doi:10.1016/S0002-9149(99)00337-9. PMID 10468091.