| Carotid body | |
|---|---|
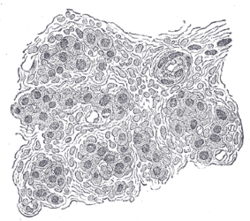 Section of part of human carotid body. Highly magnified. Numerous blood vessels are seen in section among the cells. | |
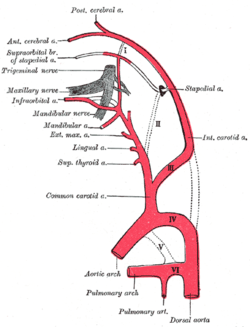 Diagram showing the origins of the main branches of the carotid arteries. | |
| Details | |
| Nerve | Branch of glossopharyngeal nerve to carotid sinus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | glomus caroticum |
| MeSH | D002344 |
| TA98 | A12.2.04.007 |
| TA2 | 3886 |
| FMA | 50095 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The carotid body is a small cluster of peripheral chemoreceptor cells and supporting sustentacular cells situated at the bifurcation of each common carotid artery in its tunica externa.[1][2]
The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arterial blood flowing through it, mainly the partial pressure of arterial oxygen, but also of carbon dioxide. It is also sensitive to changes in blood pH, and temperature.
- ^ "Carotid Body and Carotid Sinus -- General Information". Iowa Head and Neck Protocols. medicine.uiowa.edu. Retrieved 23 October 2019.
- ^ Hall, John Edward (20 May 2015). Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology (13th ed.). Philadelphia, PA. ISBN 978-1-4557-7005-2. OCLC 900869748.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)