Protein found in humans
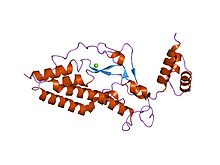
Caspase-activated DNase (CAD ) or DNA fragmentation factor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DFFB gene .[ 5] [ 6] [ 7]
^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000169598 – Ensembl , May 2017^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029027 – Ensembl , May 2017^ "Human PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ Liu X, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X (April 1997). "DFF, a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis" . Cell . 89 (2): 175–84. doi :10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80197-X PMID 9108473 . S2CID 14800864 . ^ Halenbeck R, MacDonald H, Roulston A, Chen TT, Conroy L, Williams LT (April 1998). "CPAN, a human nuclease regulated by the caspase-sensitive inhibitor DFF45" . Current Biology . 8 (9): 537–40. Bibcode :1998CBio....8..537H . doi :10.1016/S0960-9822(98)79298-X PMID 9560346 . S2CID 9837862 . ^ "Entrez Gene: DFFB DNA fragmentation factor, 40kDa, beta polypeptide (caspase-activated DNase)" .