This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2020) |
| Cauda equina | |
|---|---|
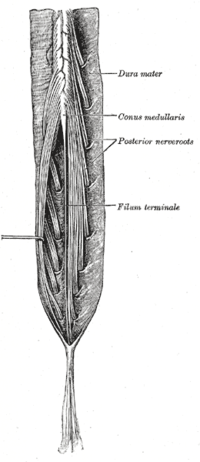 Cauda equina and filum terminale seen from behind. | |
 Human caudal spinal cord anterior view | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Iliolumbar artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cauda equina |
| MeSH | D002420 |
| TA98 | A14.2.00.036 |
| TA2 | 6163 |
| FMA | 52590 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The cauda equina (from Latin tail of horse) is a bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consisting of the second through fifth lumbar nerve pairs, the first through fifth sacral nerve pairs, and the coccygeal nerve, all of which arise from the lumbar enlargement and the conus medullaris of the spinal cord. The cauda equina occupies the lumbar cistern, a subarachnoid space inferior to the conus medullaris. The nerves that compose the cauda equina innervate the pelvic organs and lower limbs to include motor innervation of the hips, knees, ankles, feet, internal anal sphincter and external anal sphincter. In addition, the cauda equina extends to sensory innervation of the perineum and, partially, parasympathetic innervation of the bladder.[1]
- ^ "LSUHSC School of Medicine - Search Results". www.medschool.lsuhsc.edu.