This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2021) |
Central India Agency | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1854–1947 | |||||||||||||||
 The Central India Agency in the Indian Empire in 1942 | |||||||||||||||
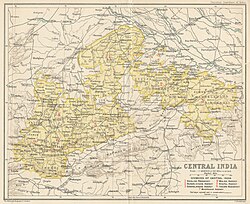 Detailed map of Central India Agency in 1909 before separation of Gwalior Residency | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | Indore | ||||||||||||||
| States under AGG for Central India | |||||||||||||||
| Government | Indirect imperial rule over a group of hereditary monarchies | ||||||||||||||
| Agent to the Governor-General | |||||||||||||||
• 1854–1857 (first) | Sir Robert Hamilton[1] | ||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
• Merger of previous political offices | 1854 | ||||||||||||||
| 1947 | |||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
| 1901 | 200,452 km2 (77,395 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
• 1901 | 9,261,907 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Central India". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. | |||||||||||||||

The Central India Agency was created in 1854, by amalgamating the Western Malwa Agency with other smaller political offices which formerly reported to the Governor-General of India. The agency was overseen by a political agent who maintained relations of the Government of India with the princely states and influence over them on behalf of the Governor-General. The headquarters of the agent were at Indore.
- ^ Madhya Pradesh District Gazetteers: Supplement.
A few weeks before the out – break at Meerut took place, Sir Robert Hamilton, the first Agent to the Governor – General in Central India, obtained leave.