| Central Provinces | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of British India | |||||||||||
| 1861–1903 | |||||||||||
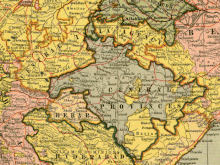 Central Provinces and Berar in 1903, before the 1905 changes to the eastern boundary | |||||||||||
| Capital | Nagpur (primary capital) Pachmarhi, Hoshangabad district (summer capital) | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Merger of the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories and Nagpur Province | 1861 | ||||||||||
• Nimar added to Central Provinces | 1864 | ||||||||||
• Creation of the Central Provinces and Berar | 1903 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Central Provinces and Berar". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 5 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 681–3. | |||||||||||

The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Nagpur was the primary winter capital while Pachmarhi served as the regular summer retreat. It became the Central Provinces and Berar in 1903.
The Central Provinces was formed in 1861 by the merger of the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories and Nagpur Province. The district of Nimar which was administered by the Central India Agency was added in 1864.[1] It was almost an island encircled by a sea of "native States" such as Bhopal State and Rewa State to the north, the Chota Nagpur States and Kalahandi State to the east, and the Nizam's territories of Hyderabad to the south and Berar to the west.[2]
- ^ Pateriya, Raghaw Raman (12 August 1991). Provincial Legislatures and the National Movement. New Delhi: Northern Book Centre. ISBN 81-85119-58-9.
- ^ Philip F. McEldowney (1980). Colonial Administration and Social Developments in middle India: The Central Provinces, 1861-1921 - Ph. D. Dissertation. University of Virginia.

