| Chacoan peccary | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male at the Phoenix Zoo | |

| |
| Female at the San Diego Zoo | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Tayassuidae |
| Genus: | Catagonus |
| Species: | C. wagneri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Catagonus wagneri (Rusconi, 1930)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Parachoerus wagneri Rusconi, 1930 | |
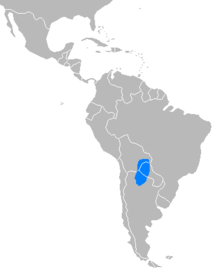
The Chacoan peccary or tagua (Catagonus wagneri or Parachoerus wagneri) is the last extant species of the genus Catagonus;[3] it is a peccary found in the Gran Chaco of Paraguay, Bolivia, and Argentina. Approximately 3,000 remain in the world.
The Chacoan peccary was first described in 1930 based on fossils and was originally thought to be an extinct species. In 1971, the animal was discovered to still be alive in the Chaco region, in the Argentine province of Salta. The species was well-known to the native people, but it took a while for Western scientists to acknowledge its existence; it is known locally as the tagua. Because it was originally described as extinct before its "rediscovery", it is an example of a Lazarus taxon.
- ^ Altrichter, M.; Taber, A.; Noss, A.; Maffei, L.; Campos, J. (2015). "Catagonus wagneri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4015A72587993. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4015A72587993.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ^ "Fossilworks: Catagonus". fossilworks.org. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 2016-05-01.
