| |
 3D model of chaconine using MolView
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
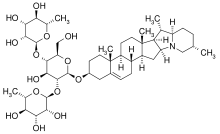
Solanid-5-en-3β-yl α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,2′S,3R,3′R,4R,4′R,5R,5′R,6S,6′S)-2,2′-{[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-4-Hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-{[(2S,4aR,4bS,6aS,6bR,7S,7aR,10S,12aS,13aS,13bS)-4a,6a,7,10-tetramethyl-1,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,6a,6b,7,7a,8,9,10,11,12a,13,13a,13b,14-icosahydro-2H-naphtho[2′,1′:4,5]indeno[1,2-b]indolizin-2-yl]oxy}oxane-3,5-diyl]bis(oxy)}bis(6-methyloxane-3,4,5-triol) | |
| Other names
α-Chaconine, Chaconine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 77396 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.161.828 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C45H73NO14 | |
| Molar mass | 852.072 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 243 °C (469 °F; 516 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H361 | |
| P203, P280, P318, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
α-Chaconine is a steroidal glycoalkaloid that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae. It is a natural toxicant produced in green potatoes and gives the potato a bitter taste.[2] Tubers produce this glycoalkaloid in response to stress, providing the plant with insecticidal and fungicidal properties.[2] It belongs to the chemical family of saponins. Since it causes physiological effects on individual organism, chaconine is considered to be defensive allelochemical.[3] Solanine is a related substance that has similar properties.
- ^ "alpha-Chaconine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ a b Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Nawrot, P.S. "Toxin profile: Solanine and Chaconine IPCS, INCHEM". Archived from the original on 2001-02-25. Retrieved 2021-03-15.
- ^ Saponins used in traditional and modern medicine. Boston, MA: Springer. 1996. pp. 277–295. ISBN 978-1-4899-1369-2.