| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
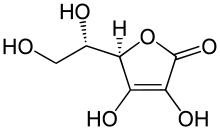
| IUPAC name
(5R)-[(1S)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5H)-one
| |
| Other names
Vitamin C
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E300 (antioxidants, ...) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O6 | |
| Molar mass | 176.124 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White or light yellow solid |
| Density | 1.65 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 190 to 192 °C (374 to 378 °F; 463 to 465 K) decomposes |
| 330 g/L | |
| Solubility | Insoluble in diethyl ether, chloroform, benzene, petroleum ether, oils, fats |
| Solubility in ethanol | 20 g/L |
| Solubility in glycerol | 10 g/L |
| Solubility in propylene glycol | 50 g/L |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.10 (first), 11.6 (second) |
| Pharmacology | |
| A11GA01 (WHO) G01AD03 (WHO), S01XA15 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
11.9 g/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | JT Baker |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula C
6H
8O
6, originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.
Ascorbic acid exists as two enantiomers (mirror-image isomers), commonly denoted "l" (for "levo") and "d" (for "dextro"). The l isomer is the one most often encountered: it occurs naturally in many foods, and is one form ("vitamer") of vitamin C, an essential nutrient for humans and many animals. Deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy, formerly a major disease of sailors in long sea voyages. It is used as a food additive and a dietary supplement for its antioxidant properties. The "d" form can be made via chemical synthesis, but has no significant biological role.
