| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
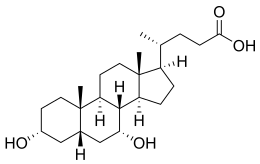
| IUPAC name
3α,7α-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(4R)-4-[(1R,3aS,3bR,4R,5aS,7R,9aS,9bS,11aR)-4,7-Dihydroxy-9a,11a-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-yl]pentanoic acid | |
| Other names
Chenodiol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.803 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H40O4 | |
| Molar mass | 392.57 g/mol |
| Melting point | 165 to 167 °C (329 to 333 °F; 438 to 440 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| A05AA01 (WHO) | |
| License data | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA; also known as chenodesoxycholic acid, chenocholic acid and 3α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid) is a bile acid. Salts of this carboxylic acid are called chenodeoxycholates. Chenodeoxycholic acid is one of the main bile acids.[1][2][3] It was first isolated from the bile of the domestic goose, which gives it the "cheno" portion of its name (Greek: χήν = goose).[4]
- ^ Russell DW (2003). "The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72: 137–74. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161712. PMID 12543708.
- ^ Bhagavan, N.V.; Ha, Chung-Eun (2015). "Gastrointestinal Digestion and Absorption". Essentials of Medical Biochemistry. pp. 137–164. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-416687-5.00011-7. ISBN 9780124166875.
- ^ Dawson, PA; Karpen, SJ (June 2015). "Intestinal transport and metabolism of bile acids". Journal of Lipid Research. 56 (6): 1085–99. doi:10.1194/jlr.R054114. PMC 4442867. PMID 25210150.
- ^ Carey MC (December 1975). "Editorial: Cheno and urso: what the goose and the bear have in common". N. Engl. J. Med. 293 (24): 1255–7. doi:10.1056/NEJM197512112932412. PMID 1186807.