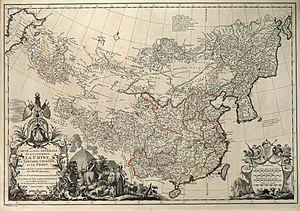

Chinese Tartary (Chinese: 中國韃靼利亞; pinyin: Zhōngguó Dádálìyà or Chinese: 中属鞑靼利亚; pinyin: Zhōng shǔ Dádálìyà) is an archaic geographical term referring to the regions of Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang (also referred to as Chinese Turkestan), and Tibet under the rule of the Qing dynasty of China. The geographical extent of Chinese Tartary largely corresponds with that of the "Feudatory Regions" (Chinese: 藩部; pinyin: fānbù), as defined by the Qing court. The term "Tartar" was used by Europeans to refer to ethnicities living in northern, northeastern, and western China, including the Mongols, Manchus, Tibetans, and Central Asians. Some definitions include the Japanese (as indicated in violet on the map below). The regions are now more commonly referred to by scholars as Inner Asia.