This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (June 2013) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets), IM, IV, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100%[1] |
| Metabolism | Extensive hepatic |
| Onset of action | 15–30 min (oral)[2] |
| Elimination half-life | ~14 hours[2] |
| Excretion | Kidney[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.383 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
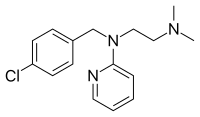
| Formula | C16H20ClN3 |
| Molar mass | 289.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Chloropyramine is a classical first-generation antihistamine drug approved in Eastern European countries (and Russia, but not in Central European countries) for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, and other atopic (allergic) conditions. Related indications for clinical use include angioedema (Quincke's edema), allergic reactions to insect bites, food and drug allergies, and anaphylactic shock.
Chloropyramine is known as a competitive reversible H1 receptor antagonist (also known as an H1 inverse agonist), meaning that it exerts its pharmacological action by competing with histamine for the H1 subtype histamine receptor. By blocking the effects of histamine, the drug inhibits the vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and tissue edema associated with histamine release in the tissue. The H1 antagonistic properties of chloropyramine can be used by researchers for the purposes of blocking the effects of histamine on cells and tissues. In addition, chloropyramine has some anticholinergic properties.[1]
Chloropyramine's anticholinergic properties and the fact that it can pass through the blood–brain barrier are linked to its clinical side effects: drowsiness, weakness, vertigo, fatigue, dryness in the mouth, constipation, and rarely — visual disturbances and increase of intraocular pressure.
- ^ a b "Chloropyramine Tablets for Oral Use. Prescribing Information". State Register of Medicines (in Russian). Ozon OOO. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^ a b c "Хлоропирамин (Chloropyraminum)" (in Russian).