| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
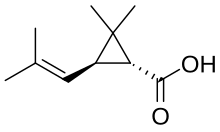
2,2-Dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.788 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16O2 | |
| Molar mass | 168.236 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 17 °C (63 °F; 290 K) (1R,3R) or (+)-trans |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chrysanthemic acid is an organic compound that is related to a variety of natural and synthetic insecticides. It is related to the pyrethrin I and II, as well as the pyrethroids. One of the four stereoisomers, (1R,3R)- or (+)-trans-chrysanthemic acid (pictured), is the acid part of the ester pyrethrin I, which occurs naturally in the seed cases of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium. Many synthetic pyrethroids, for example the allethrins, are esters of all four stereoisomers.[1] Staudinger and Ružička named chrysanthemic acid in 1924.[2]
- ^ Faust, Rüdiger (2001). "Fascinating Natural and Artificial Cyclopropane Architectures". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 40 (12): 2251–2253. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20010618)40:12<2251::AID-ANIE2251>3.0.CO;2-R. PMID 11433485.
- ^ H. Staudinger, L. Ružička: "Insektentotende Stoffe H. Zur Konstitution der Chrysanthemummonocarbonsiiure und -dicarbonsiiure", Helv. Chem. Acta 7 (1924) 201