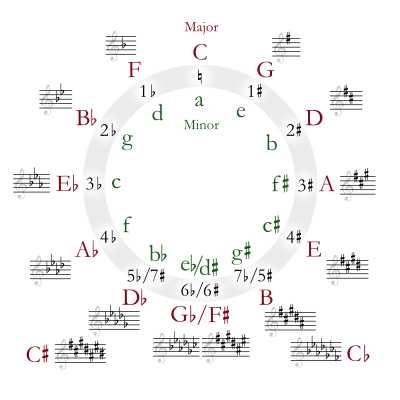
In music theory, the circle of fifths (sometimes also cycle of fifths) is a way of organizing pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths. Starting on a C, and using the standard system of tuning for Western music (12-tone equal temperament), the sequence is: C, G, D, A, E, B, F♯/G♭, C♯/D♭, G♯/A♭, D♯/E♭, A♯/B♭, F, and C. This order places the most closely related key signatures adjacent to one another.
Twelve-tone equal temperament tuning divides each octave into twelve equivalent semitones, and the circle of fifths leads to a C seven octaves above the starting point. If the fifths are tuned with an exact frequency ratio of 3:2 (the system of tuning known as just intonation), this is not the case (the circle does not "close").