This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2012) |
 |
| Longitude (λ) |
|---|
| Lines of longitude appear vertical with varying curvature in this projection, but are actually halves of great ellipses, with identical radii at a given latitude. |
| Latitude (φ) |
| Lines of latitude appear horizontal with varying curvature in this projection; but are actually circular with different radii. All locations with a given latitude are collectively referred to as a circle of latitude. |
|
|
| Geodesy |
|---|
 |

A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth (ignoring elevation) at a given latitude coordinate line.
Circles of latitude are often called parallels because they are parallel to each other; that is, planes that contain any of these circles never intersect each other. A location's position along a circle of latitude is given by its longitude. Circles of latitude are unlike circles of longitude, which are all great circles with the centre of Earth in the middle, as the circles of latitude get smaller as the distance from the Equator increases. Their length can be calculated by a common sine or cosine function. For example, the 60th parallel north or south is half as long as the Equator (disregarding Earth's minor flattening by 0.335%), stemming from . On the Mercator projection or on the Gall-Peters projection, a circle of latitude is perpendicular to all meridians.[1] On the ellipsoid or on spherical projection, all circles of latitude are rhumb lines, except the Equator.
The latitude of the circle is approximately the angle between the Equator and the circle, with the angle's vertex at Earth's centre. The Equator is at 0°, and the North Pole and South Pole are at 90° north and 90° south, respectively. The Equator is the longest circle of latitude and is the only circle of latitude which also is a great circle. As such, it is perpendicular to all meridians.
There are 89 integral (whole degree) circles of latitude between the Equator and the poles in each hemisphere, but these can be divided into more precise measurements of latitude, and are often represented as a decimal degree (e.g. 34.637° N) or with minutes and seconds (e.g. 22°14'26" S).
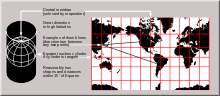
On a map, the circles of latitude may or may not be parallel, and their spacing may vary, depending on which projection is used to map the surface of the Earth onto a plane. On an equirectangular projection, centered on the equator, the circles of latitude are horizontal, parallel, and equally spaced. On other cylindrical and pseudocylindrical projections, the circles of latitude are horizontal and parallel, but may be spaced unevenly to give the map useful characteristics. For instance, on a Mercator projection the circles of latitude are more widely spaced near the poles to preserve local scales and shapes, while on a Gall–Peters projection the circles of latitude are spaced more closely near the poles so that comparisons of area will be accurate. On most non-cylindrical and non-pseudocylindrical projections, the circles of latitude are neither straight nor parallel.
Arcs of circles of latitude are sometimes used as boundaries between countries or regions where distinctive natural borders are lacking (such as in deserts), or when an artificial border is drawn as a "line on a map", which was made in massive scale during the 1884 Berlin Conference, regarding huge parts of the African continent. North American nations and states have also mostly been created by straight lines, which are often parts of circles of latitudes. For instance, the northern border of Colorado is at 41° N while the southern border is at 37° N. Roughly half the length of the border between the United States and Canada follows 49° N.
- ^ Kher, Aparna. "What Are Longitudes and Latitudes?". timeanddate.com. Retrieved April 15, 2020.

