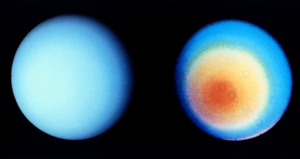
The climate of Uranus is heavily influenced by both its lack of internal heat, which limits atmospheric activity, and by its extreme axial tilt, which induces intense seasonal variation. Uranus's atmosphere is remarkably bland in comparison to the other giant planets which it otherwise closely resembles.[1][2] When Voyager 2 flew by Uranus in 1986, it observed a total of ten cloud features across the entire planet.[3][4] Later observations from the ground or by the Hubble Space Telescope made in the 1990s and the 2000s revealed bright clouds in the northern (winter) hemisphere. In 2006 a dark spot similar to the Great Dark Spot on Neptune was detected.[5]
- ^ Sromovsky & Fry 2005.
- ^ Pierrehumbert, Raymond T. (2 December 2010). Principles of Planetary Climate. Cambridge University Press. p. 20. ISBN 9781139495066. Retrieved 19 November 2014.
- ^ Smith Soderblom et al. 1986.
- ^ Lakdawalla 2004.
- ^ Hammel Sromovsky et al. 2009.