 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Variable, 92–97% at therapeutic concentrations |
| Metabolism | Hydrolyzed to clofibric acid; hepatic glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | Highly variable; average 18–22 hours. Prolonged in renal failure |
| Excretion | Renal, 95 to 99% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.253 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
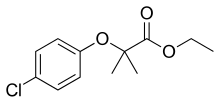
| Formula | C12H15ClO3 |
| Molar mass | 242.70 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Boiling point | 148 °C (298 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Clofibrate (trade name Atromid-S) is a lipid-lowering agent used for controlling the high cholesterol and triacylglyceride level in the blood. It belongs to the class of fibrates. It increases lipoprotein lipase activity to promote the conversion of VLDL to LDL, and hence reduce the level of VLDL. It can increase the level of HDL as well.
It was patented in 1958 by Imperial Chemical Industries and approved for medical use in 1963.[1] Clofibrate was discontinued in 2002 due to adverse effects.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 474. ISBN 9783527607495.