| Coastal taipan | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Elapidae |
| Genus: | Oxyuranus |
| Species: | O. scutellatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Oxyuranus scutellatus | |
| |
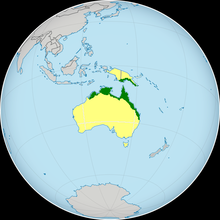
| Distribution of Oxyuranus scutellatus in green | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
The coastal taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus), or common taipan,[4] is a species of extremely venomous snake in the family Elapidae. Described by Wilhelm Peters in 1867, the species is native to the coastal regions of northern and eastern Australia and the island of New Guinea. The second-longest venomous snake in Australia, the coastal taipan averages around 2.0 m (6.6 ft) long, with the longest specimens reaching 2.9 m (9.5 ft) in length. It has light olive or reddish-brown upperparts, with paler underparts. The snake is considered to be a least-concern species according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
The coastal taipan is found in a wide range of habitats, from monsoon forests to open woodland, as well as human-modified habitats such as sugarcane fields. It mainly hunts and eats small mammals, and opportunistically takes bird prey. The species is oviparous.
According to most toxicological studies, this species is the third-most venomous land snake in the world after the inland taipan and eastern brown snake. Its venom is predominantly neurotoxic and coagulopathic.
- ^ Tallowin, O.; Parker, F.; O'Shea, M.; Hoskin, C.; Vanderduys, E.; Amey, A.; Couper, P. (2018). "Oxyuranus scutellatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T42493166A42493177. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T42493166A42493177.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "Oxyuranus scutellatus (PETERS, 1867)". The Reptile Database. Retrieved 16 February 2012.
- ^ Australian Biological Resources Study (19 March 2013). "Subspecies Oxyuranus scutellatus scutellatus (Peters, 1867)". Australian Faunal Directory. Canberra, Australian Capital Territory: Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts, Australian Government. Retrieved 28 July 2021.
- ^ "CSL Taipan Antivenom". CSL Antivenom Handbook. www.toxinology.com. Retrieved 7 December 2011.
