| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cobalt(II) fluoride
| |
| Other names
cobalt difluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.044 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CoF2 | |
| Molar mass | 96.93 g/mol |
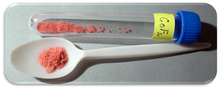
| Appearance | Red crystalline solid |
| Density | 4.46 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.22 g/cm3 (tetrahydrate) |
| Melting point | 1,217 °C (2,223 °F; 1,490 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,400 °C (2,550 °F; 1,670 K) |
| 1.4 g/100 mL (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in HF insoluble in alcohol, ether, benzene |
| +9490.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
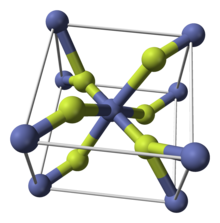
| tetragonal (anhydrous) orthorhombic (tetrahydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
oral (rat): 150 mg/kg |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
cobalt(II) oxide, cobalt(II) chloride |
Other cations
|
iron(II) fluoride, nickel(II) fluoride |
Related compounds
|
cobalt trifluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Cobalt(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula (CoF2). It is a pink crystalline solid compound[1][2] which is antiferromagnetic at low temperatures (TN=37.7 K)[3] The formula is given for both the red tetragonal crystal, (CoF2), and the tetrahydrate red orthogonal crystal, (CoF2·4H2O). CoF2 is used in oxygen-sensitive fields, namely metal production. In low concentrations, it has public health uses. CoF2 is sparingly soluble in water. The compound can be dissolved in warm mineral acid, and will decompose in boiling water. Yet the hydrate is water-soluble, especially the di-hydrate CoF2·2H2O and tri-hydrate CoF2·3H2O forms of the compound. The hydrate will also decompose with heat.
Like some other metal difluorides, CoF2 crystallizes in the rutile structure, which features octahedral Co centers and planar fluorides.[4]
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik (2002), Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals, McGraw-Hill Professional, ISBN 978-0-07-049439-8
- ^ Pashkevich, D. S.; Radchenko S. M.; Mukhortov, D. A., "Article title Heat Exchange between Cobalt(II) Fluoride Powder and the Wall of Rotating Cylinder" (PDF), Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, Consultants Bureau, ISSN 1070-4272, archived from the original (PDF) on 2004-09-29, retrieved 2007-03-07
- ^ Ashcroft/Mermin: Solid State Physics (Tab. 33.2)
- ^ Stout, J. W.; Reed, Stanley A. (1954). "The Crystal Structure of MnF2, FeF2, CoF2, NiF2 and ZnF2". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 76 (21): 5279–5281. doi:10.1021/ja01650a005.
