 Layout of the IBM-949 code page | |
| Alias(es) |
|
|---|---|
| Language(s) | Korean |
| Created by | IBM |
| Classification | Extended ISO 646, variable-width encoding, CJK encoding |
| Extends | EUC-KR |
| Preceded by | Code page 944 |
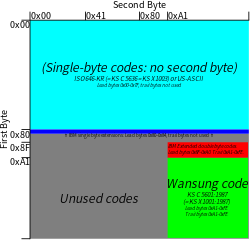
IBM code page 949 (IBM-949) is a character encoding which has been used by IBM to represent Korean language text on computers. It is a variable-width encoding which represents the characters from the Wansung code defined by the South Korean standard KS X 1001 in a format compatible with EUC-KR, but adds IBM extensions for additional hanja, additional precomposed Hangul syllables, and user-defined characters.
Giving values in hexadecimal, bytes 0x00 through 0x7F are used for single byte KS X 1003 (ISO 646:KR) characters, a similar set to ASCII but with a won sign rather than a backslash. Bytes 0x80 through 0x84 are used for IBM single byte extension characters. Lead bytes 0x8F through 0xA0 are used for IBM double byte extension characters. Lead bytes 0xA1 through 0xFE are used for Wansung code (KS X 1001 characters in EUC-KR form, double byte), but with some unused space opened up for user-defined use.
Although both are sometimes named "cp949", IBM-949 is different from Windows code page 949 (IBM-1363), which is Microsoft's Unified Hangul Code, a different extension of EUC-KR. It should also not be confused with IBM's implementation of plain EUC-KR (IBM-970). Code page 949 in OS/2 is the IBM code page; however, a third-party patch exists to change this.[1]
- ^ Borgendale, Ken. "OS/2 Codepage and Keyboard Display Tools".