 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /koʊˈlɛstərəmiːn/, /koʊlɪˈstaɪrəmiːn/ |
| Trade names | Questran, Cholybar, Olestyr, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682672 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | low |
| Protein binding | unknown |
| Metabolism | bile acids |
| Elimination half-life | 1 hour |
| Excretion | Faecal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.143 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Molar mass | In average, exceeds 1×106 g/mol |
| | |
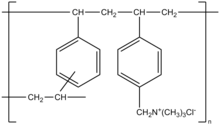
Colestyramine (INN) or cholestyramine (USAN) (trade names Questran, Questran Light, Cholybar, Olestyr) is a bile acid sequestrant, which binds bile in the gastrointestinal tract to prevent its reabsorption. It is a strong ion exchange resin, which means it can exchange its chloride anions with anionic bile acids in the gastrointestinal tract and bind them strongly in the resin matrix. The functional group of the anion exchange resin is a quaternary ammonium group attached to an inert styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer.
Colestyramine removes bile acids from the body by forming insoluble complexes with bile acids in the intestine, which are then excreted in the feces.[1] As a result of this loss of bile acids, more plasma cholesterol is converted to bile acids in the liver to normalise levels.[1] This conversion of cholesterol into bile acids lowers plasma cholesterol levels.[1]