A number of different spacecraft have been used to carry cargo to and from space stations. This list does not include crewed spacecraft.
| Spacecraft under development | |
| Spacecraft is operational | |
| Retired spacecraft | |
| § | Pressurized / Unpressurized payload capacity |
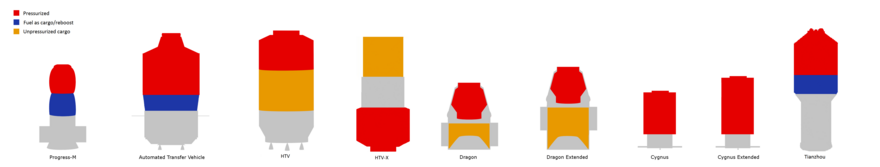
| Spacecraft | Origin | Manufacturer | Launch vehicle | Length (m) | Dry mass (kg) | Launch mass (kg) | Payload (kg) § | Payload volume (m3) | Return payload (kg) § | Diameter (m) | Generated power (W) | Automated docking | Status (No. flights) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TKS | TsKBM | Proton-K | 17.51 | 13,688 | 21,620 | 12,600 | 4.15 | 2,400 | No | Retired (4) | |||
| Progress 7K-TG | Energia | Soyuz-U | None | No | Retired (43) | ||||||||
| Progress-M (11F615A55) | Energia | Soyuz-U Soyuz-U2 |
7.2 | 7,130 | 2,600 | 7.6 | 150[a] | 2.72 | 600[1] | Yes | Retired (66) | ||
| Progress-M1 | Energia | Soyuz-U Soyuz-FG |
None | Yes | Retired (11) | ||||||||
| Progress-M (11F615A60) | Energia | Soyuz-U | 7.2 | 7,150 | 2,230 | 7.6 | None | 2.72 | 700 | Yes | Retired (27 + 2 failed) | ||
| Cygnus | Orbital | Antares | 5.14 | 1,500[2] | 2,000[2] | 18.9[2] | None | 3.07 | 3,500[3] | No | Retired (3 + 1 failed) | ||
| Dragon 1 | SpaceX | Falcon 9 | 6.1 | 4,200[4] | 10,200[b] | 3,310 (max) 2,200 (ave)[c][5] | 10.0 / (14 or 34)[d][6] | 3,000[e][7] | 3.7 | 2,000[8] | No | Retired (19 + 1 failed)[9] | |
| ATV | Airbus | Ariane 5ES | 10.3 | 10,470[10] | 20,750[10] | 7,667[10] | 48 | None | 4.5 | 3,800[11] | Yes | Retired (5) | |
| HTV | JAXA | H-IIB | 10 | 10,500[12] | 16,500[12] | 3,000 / 1,000[12] | 14 / 16[12] | 20[f][13] | 4.4 | 200 | No | Retired (9) | |
| Tianzhou (basic) |
CAST | Long March 7 | 10.6 | 13,500 | 6,900[g][14] | 18.1 | None | 3.35 | Yes | Retired (5) | |||
| Progress-MS | Energia | Soyuz 2.1a | 7.2 | 7,150 | 2,230 | None | Yes | Operational[15] | |||||
| Cargo Dragon 2 | SpaceX | Falcon 9 | 8.1 | 6,400 | 3,307[5] | 9.3 / 37 | 2,507[5] | 4.0 | Yes | Operational | |||
| Enhanced Cygnus | Northrop Grumman | Antares[h] | 6.39 | 1,800[16] | 3,750 | 27[16] | None | 3.07 | 3,500 | No | Operational | ||
| Tianzhou (improved) | CAST | Long March 7 | 10.6 | 14,000 | 7,400[i][14] | 22.5 (~40 total) | None | 3.35 | Yes | Operational | |||
| Dream Chaser | Sierra Space | Vulcan Centaur | 16.8[17] | 5,000 / 500[18] | 1,750[18] | ? | Development | ||||||
| HTV-X | JAXA | H3[19] | 10[j] | 8,300 | 16,000, combined[20] | 4,069 / 1,750 | 78[k] | None | 4.4 | 1,000 | No[l] | Development[21] | |
| Cygnus Mission B | Northrop Grumman | Antares | 7.89 | 5,000 | 36 | None | 3.07 | 3,500 | Planned | Under construction[22] | |||
| Dragon XL | SpaceX | Falcon Heavy | 5,000[23] | None | Yes[23] | Development[24] | |||||||
| Argo | Rocket Factory Augsburg | 3,400 | <13 | ≥1,000[25] | Yes | Development[26] | |||||||
| NYX | The Exploration Company | 4,000 | 2,500 / 100[27] | Yes | Development[28] |
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ "Progress M". Archived from the original on 10 July 2009. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ^ a b c "Cygnus Fast Sheet" (PDF). Orbital Sciences Co. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ "The Annual Compendium of Commercial Space Transportation: 2012" (PDF). Federal Aviation Administration. February 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "SpaceX Brochure v7" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ^ a b c Audit of Commercial Resupply Services to the International Space Station Archived 30 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Overall Dragon Capabilities" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-01-04. Retrieved 2016-07-21.
- ^ "Falcon 9 launches Dragon on CRS-1 mission to the ISS". 7 October 2012.
- ^ "Dragonlab Datasheet" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ^ Clark, Stephen. "With successful splashdown, SpaceX retires first version of Dragon spacecraft – Spaceflight Now". Retrieved 2020-04-10.
- ^ a b c "ESA Automated Transfer Vehicle". ESA. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ "ATV Utilization Relevant Data" (PDF). Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ^ a b c d "JAXA transition examination of the new space station supply machine (HTV-X)" (PDF). JAXA. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- ^ "HTV 搭載小型回収カプセルの開発" (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. 12 November 2014. Retrieved 2016-10-21.
- ^ a b Jones, Andrew (10 May 2023). "Tianzhou-6 cargo spacecraft reaches China's Tiangong space station". spacenews.com. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Upgraded Progress MS docks with the ISS". NASASpaceflight.com. 23 December 2015. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- ^ a b "Cygnus Spacecraft Information". Spaceflight101. Archived from the original on 2015-09-09.
- ^ Meredith Garofalo (February 2, 2024). "Sierra Space unveils Dream Chaser space plane ahead of 1st flight to ISS (video)". Space.com.
- ^ a b Brian Wang (January 22, 2024). "Sierra Space Spaceplane and Space Stations". Next Big Future.
- ^ "H3,H-IIA/Bのミッション割当て(案)" (PDF) (in Japanese). MEXT. 8 March 2016. Retrieved 2016-03-10.
- ^ "HTV-X, the new unmanned spacecraft now being developed by JAXA". JAXA. Retrieved November 23, 2022.
- ^ Funding for HTV-X development was included in the FY 2016 JAXA budget
- ^ Parsonson, Andrew (2024-05-14). "Thales Alenia Space Delivers Pressurized Module for 21st Cygnus Spacecraft". European Spaceflight. Retrieved 2024-06-20.
- ^ a b "NASA picks SpaceX to deliver cargo to Gateway station in lunar orbit – Spaceflight Now". Retrieved 2023-06-07.
- ^ Foust, Jeff (2023-02-24). "NASA plans to start work this year on first Gateway logistics mission". SpaceNews. Retrieved 2023-06-07.
- ^ Parsonson, Andrew (20 September 2023). "RFA-Led Consortium Submit Argo for ESA Commercial Cargo Initiative". European Spaceflight. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- ^ Rocket Factory Augsburg. "One (c)argo capsule, tons of possibilities!". Twitter. Retrieved 21 September 2023.
- ^ Parsonson, Andrew (23 February 2022). "The Exploration Company aims to offer Europe independent access to space". European Spaceflight. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- ^ The Exploration Company. "Missions". Retrieved 22 September 2023.



