| Constitution Protection Region of Southern Fujian 閩南護法區 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| de facto autonomous region of the Republic of China | |||||||||
| 1918–1920 | |||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||
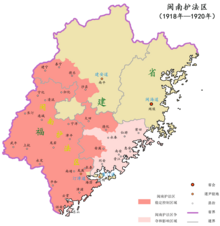 Map of the Constitution Protection Region of Southern Fujian Areas stably controlled by the Constitution Protection Region of Southern Fujian
Areas contested and influenced by the Constitution Protection Region of Southern Fujian
The rest of Fujian Province | |||||||||
| Capital | Longxi (Zhangzhou) | ||||||||
| Government | Constitutional Protection Junta | ||||||||
| • Type | Anarchist civil-military government | ||||||||
| • Motto | "Fraternity, Liberty, Equality, Mutual aid" “博愛、自由、平等、互助” | ||||||||
| Commander-in-chief | |||||||||
• 1918–1920 | Chen Jiongming | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1 September 1918 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 12 August 1920 | ||||||||
| Subdivisions | |||||||||
| • Type | County | ||||||||
| • Units | 26 counties | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | China ∟Fujian | ||||||||
The Constitution Protection Region of Southern Fujian (Chinese: 閩南護法區; pinyin: Mǐnnán hùfǎ qū)[1][a][b] was a de facto autonomous region of Republic of China established by the "Guangdong Army to assist Fujian" (Chinese: 援閩粵軍; pinyin: Yuánmǐn yuèjūn)[c] led by General Chen Jiongming. The regional administration controlled 26 counties of southern and western Fujian, with Zhangzhou as its capital, where it implemented some policies with anarchist characteristics.
The regional administration was established during the Constitutional Protection Movement, when Chen's forces fought to defeat the Northern warlords of the Anhui and Zhili cliques, and reassert constitutionalism in southern China. After moving into Fujian and fighting against the northern forces of Li Houji, Chen's Guangdong Army established control over the southern part of the region. Zhangzhou subsequently became a centre of the New Culture Movement, which established newspapers to propagate its ideas of "liberty", equality", "fraternity" and "mutual aid". Anarchists and communists were also attracted to the region, where under Chen's protection, they were able to agitate and organize with full freedom of speech and freedom of association.
In the capital of Zhangzhou, the city's defensive walls were demolished in order to make way for carriageways and public parks. The administration also established a comprehensive education system, sending several students to France as part of the work-study program. The reforms carried out were extensive and received popular support, as they improved societal infrastructure and welfare, while also keeping taxes relatively low. The reforms attracted the attention of the Russian Soviet Republic, which dispatched a representative to establish relations with the regional administration. This also drew the attention of American and British intelligence, which were worried by the rise of "Bolshevism" in the region.
With the outbreak of the Guangdong–Guangxi War, the majority of Chen's Guangdong Army left the region in order to fight against the Guangxi clique and retake control of Guangdong. For a few months, a small garrison was left behind in Southern Fujian, which was eventually handed back over to the forces of Li Houji.
- ^ Chen 1999, p. 86.
- ^ Goikhman 2013, pp. 81–82.
- ^ "漳州现99年前民国粤军地契 见证一段历史" [A 99-year-old land deed of the Republic of China's Guangdong army is found in Zhangzhou, witnessing a piece of history] (in Simplified Chinese). Taihainet. 2019-02-27. Archived from the original on 2023-04-22. Retrieved 2023-06-26.
1918年6月,陈炯明与李厚基达成划界停战协议,在粤军所占区域建立"福建护法区"(后称"闽南护法区"),首府设于漳州。
[In June 1918, Chen Jiongming and Li Houji reached a boundary ceasefire agreement, establishing the "Constitution Protection Region of Fujian" (later known as the "Constitution Protection Region of Southern Fujian") in the area occupied by the Guangdong Army, with its capital in Zhangzhou.] - ^ Guo 2020, p. 7.
- ^ Chen 1999, pp. 75–77; Goikhman 2013, p. 85.
- ^ Guo 2020, p. 7n24.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).

