| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
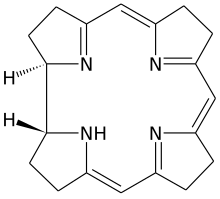
| C19H22N4 | |
| Molar mass | 306.40478 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Corrin is a heterocyclic compound. Although not known to exist on its own, the molecule is of interest as the parent macrocycle related to the cofactor and chromophore in vitamin B12. Its name reflects that it is the "core" of vitamin B12 (cobalamins). Compounds with a corrin core are known as "corrins".[1]
There are two chiral centres, which in natural compounds like cobalamin have the same stereochemistry.
- ^ Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.