| Constellation | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | Crv |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Corvi |
| Pronunciation | /ˈkɔːrvəs/, genitive /ˈkɔːrvaɪ/ |
| Symbolism | the Crow/Raven |
| Right ascension | 12h |
| Declination | −20° |
| Area | 184 sq. deg. (70th) |
| Main stars | 4 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 10 |
| Stars with planets | 3 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 3 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 1 |
| Brightest star | γ Crv (Gienah) (2.59m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | Corvids Eta Corvids |
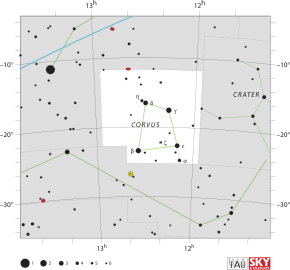
| Bordering constellations | Virgo Crater Hydra |
| Visible at latitudes between +60° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of May. | |
Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name means "crow" in Latin. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it depicts a raven, a bird associated with stories about the god Apollo, perched on the back of Hydra the water snake. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi, form a distinctive quadrilateral or cross-shape in the night sky.
With an apparent magnitude of 2.59, Gamma Corvi—also known as Gienah—is the brightest star in the constellation. It is an aging blue giant around four times as massive as the Sun. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks. Three star systems have exoplanets, and a fourth planetary system is unconfirmed. TV Corvi is a dwarf nova—a white dwarf and brown dwarf in very close orbit.