 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Rauhimbine |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.901 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
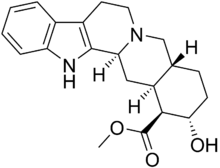
| Formula | C21H26N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 354.450 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Corynanthine, also known as rauhimbine, is an alkaloid found in the Rauvolfia and Corynanthe (including Pausinystalia) genera of plants.[1][2] It is one of the two diastereoisomers of yohimbine, the other being rauwolscine.[3][4] It is also related to ajmalicine.
Corynanthine acts as an α1-adrenergic and α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist with approximately 10-fold selectivity for the former site over the latter.[3][4] This is in contrast to yohimbine and rauwolscine which have around 30-fold higher affinity for the α2-adrenergic receptor over the α1-adrenergic receptor.[3][4] As a result, corynanthine is not a stimulant (or an aphrodisiac for that matter), but a depressant, and likely plays a role in the antihypertensive properties of Rauvolfia extracts. Like yohimbine and rauwolscine, corynanthine has also been shown to possess some activity at serotonin receptors.[5]
- ^ PHILLIPS DD, CHADHA MS (September 1955). "The alkaloids of Rauwolfia serpentina Benth". Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association. 44 (9): 553–67. doi:10.1002/jps.3030440912. PMID 13251932.
- ^ "Alkaloids from Rauvolfia canescens; Pharmaceutical Biology - 39(3):Pages 239-240 - Informa Healthcare". Pharmaceutical Biology. doi:10.1076/phbi.39.3.239.5923. S2CID 85168336.
- ^ a b c Shepperson NB, Duval N, Massingham R, Langer SZ (November 1981). "Pre- and postsynaptic alpha adrenoceptor selectivity studies with yohimbine and its two diastereoisomers rauwolscine and corynanthine in the anesthetized dog". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 219 (2): 540–6. PMID 6270312.
- ^ a b c Doxey JC, Lane AC, Roach AG, Virdee NK (February 1984). "Comparison of the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist profiles of idazoxan (RX 781094), yohimbine, rauwolscine and corynanthine". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 325 (2): 136–44. doi:10.1007/bf00506193. PMID 6144048. S2CID 24276613.
- ^ Feuerstein TJ, Hertting G, Jackisch R (May 1985). "Endogenous noradrenaline as modulator of hippocampal serotonin (5-HT)-release. Dual effects of yohimbine, rauwolscine and corynanthine as alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists and 5-HT-receptor agonists". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 329 (3): 216–21. doi:10.1007/bf00501871. PMID 2991775. S2CID 19770424.