This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (November 2021) |  |
| Cross-matching | |
|---|---|
 Compatibility testing concerning RBCs | |
| MeSH | D001788 |
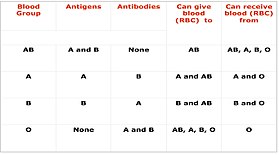
Cross-matching or crossmatching is a test performed before a blood transfusion as part of blood compatibility testing. Normally, this involves adding the recipient's blood plasma to a sample of the donor's red blood cells. If the blood is incompatible, the antibodies in the recipient's plasma will bind to antigens on the donor red blood cells. This antibody-antigen reaction can be detected through visible clumping or destruction of the red blood cells, or by reaction with anti-human globulin. Along with blood typing of the donor and recipient and screening for unexpected blood group antibodies, cross-matching is one of a series of steps in pre-transfusion testing. In some circumstances, an electronic cross-match can be performed by comparing records of the recipient's ABO and Rh blood type against that of the donor sample.[1]: 600−3 In emergencies, blood may be issued before cross-matching is complete.[2]: 263 Cross-matching is also used to determine compatibility between a donor and recipient in solid organ transplantation including heart/lung transplation.[3][4]
- ^ Turgeon, ML (2016). Linné & Ringsrud's Clinical Laboratory Science: Concepts, Procedures, and Clinical Applications (7 ed.). Elsevier Mosby. ISBN 978-0-323-22545-8.
- ^ Denise M Harmening (30 November 2018). Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices. F.A. Davis. ISBN 978-0-8036-9462-0.
- ^ Mulley W, Kanellis J (2011). "Understanding crossmatch testing in organ transplantation: A case-based guide for the general nephrologist". Nephrology. 16 (2): 125–133. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1797.2010.01414.x. PMID 21272123. S2CID 205474176. Retrieved 13 September 2020.
- ^ Flajnik, M. F.; Singh, Nevil; Holland, Steven M., eds. (2023). "CHAPTER 19 The major histocompatibility complex". Paul's fundamental immunology (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wikins. p. 585. ISBN 978-1-9751-4253-7.