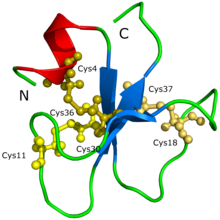
Crotamine is a toxin present in the venom of the South American rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus terrificus). It is a 42-residue-long protein containing 11 basic residues (nine lysines, two arginines) and six cysteines. It has also been isolated from the venom of North American prairie rattlesnake, Crotalus viridis viridis. It was first isolated and purified by Brazilian scientist José Moura Gonçalves, and later intensively studied by his group of collaborators at the Medical School of Ribeirão Preto of the University of São Paulo.