| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
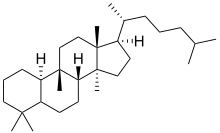
| IUPAC name
19-Nor-5ξ,9β,10α-lanostane
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bR,5aΞ,9aR,9bS,11aR)-3a,6,6,9b,11a-Pentamethyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H54 | |
| Molar mass | 414.762 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cucurbitane is a class of tetracyclic chemical compounds with formula C
30H
54 (CAS number 65441-59-0). It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, specifically triterpene. It is also an isomer of lanostane (specifically 19(10→9β)-abeolanostane), from which it differs by the formal shift of a methyl group (carbon number 19) from the 10 to the 9β position in the standard steroid numbering scheme.[1][2]
The name is applied to two stereoisomers, distinguished by the prefixes 5α- and 5β-, which differ by the handedness of the bonds at a particular carbon atom (number 5 in the standard steroid numbering scheme).[1]
-
5α-Cucurbitane
-
5β-Cucurbitane
- ^ a b "The Nomenclature of Steroids — Revised Tentative Rules". European Journal of Biochemistry. 10: 1–19. 1969. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00650.x.
- ^ Satish Kumar and Raj Kumar (1991), Dictionary of Biochemistry. Anmol Publications, India

