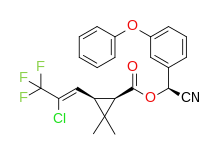
 λ-cyhalothrin (racemic)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R)-α-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1S)-cis-3-[(Z)-2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropenyl]-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate and (S)-α-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1R)-cis-3-[(Z)-2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropenyl]-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
| |
| Other names
Cyhalothrine
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.062.209 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 2588 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C23H19ClF3NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 449.85 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless solid |
| Density | 1.33 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 49.2 °C (120.6 °F; 322.3 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes before boiling |
| 0.005 mg/L [20 °C] | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Very soluble in hexane, toluene, methanol, acetone |
| log P | 5.5 |
| Acidity (pKa) | Not applicable |
| Pharmacology | |
| QP53AC06 (WHO) | |
| Hazards[2] | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H312, H330, H410 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P310, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cyhalothrin (ISO common name[3]) is an organic compound that, in specific isomeric forms, is used as a pesticide.[4] It is a pyrethroid, a class of synthetic insecticides that mimic the structure and properties of the naturally occurring insecticide pyrethrin which is present in the flowers of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium. Pyrethroids, such as cyhalothrin, are often preferred as an active ingredient in agricultural insecticides because they are more cost-effective and longer acting than natural pyrethrins. λ-and γ-cyhalothrin are now used to control insects and spider mites in crops including cotton, cereals, potatoes and vegetables.[5]
- ^ Pesticide Properties Database. "lambda-Cyhalothrin". University of Hertfordshire.
- ^ "[(R)-Cyano-(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl] 3-[(Z)-2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoroprop-1-enyl]-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylate". Retrieved 2020-02-02.
- ^ "Compendium of Pesticide Common Names". BCPC.
- ^ Pesticide Properties Database. "Cyhalothrin". University of Hertfordshire.
- ^ Metcalf, Robert L.; Horowitz, Abraham R. (2014). "Insect Control, 1. Fundamentals". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_263.
