| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
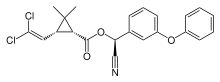
| IUPAC name
[Cyano-(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl]3-(2,2-dichloroethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.052.567 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Cypermethrin |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H19Cl2NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 416.30 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| P03BA02 (WHO) QP53AC08 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (November 2024) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Cypermethrin (CP) is a synthetic pyrethroid used as an insecticide in large-scale commercial agricultural applications as well as in consumer products for domestic purposes. It behaves as a fast-acting neurotoxin in insects. It is easily degraded on soil and plants but can be effective for weeks when applied to indoor inert surfaces. It is a non-systemic and non-volatile insecticide that acts by contact and ingestion, used in agriculture and in pest control products. Exposure to sunlight, water and oxygen will accelerate its decomposition. Cypermethrin is highly toxic to fish, bees and aquatic insects, according to the National Pesticide Information Center (NPIC) (previously National Pesticides Telecommunication Network) in the USA[1]. It is found in many household ant and cockroach killers, including Raid, Ortho, Combat, ant chalk, and some products of Baygon in Southeast Asia.
- ^ "Cypermethrin" (PDF). 5 Nov 2024.