| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
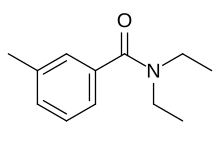
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide | |
| Other names
N,N-Diethyl-m-toluamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.682 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H17NO | |
| Molar mass | 191.27 g/mol |
| Density | 0.998 g/mL |
| Melting point | −33 °C (−27 °F; 240 K) |
| Boiling point | 288 to 292 °C (550 to 558 °F; 561 to 565 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| P03BX02 (WHO) QP53GX01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H315, H319, H402 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N,N-Diethyl-meta-toluamide, also called diethyltoluamide or DEET (/diːt/, from DET, the initials of di- + ethyl + toluamide),[1][2] is the oldest, one of the most effective, and most common active ingredients in commercial insect repellents. It is a slightly yellow oil intended to be applied to the skin or to clothing and provides protection against mosquitoes, flies, ticks, fleas, chiggers, leeches, and many other biting insects.
- ^ "DEET". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2023-06-04.
- ^ Plumlee KH (2004-01-01), Plumlee KH (ed.), "Chapter 21 - Insecticides and Molluscicides", Clinical Veterinary Toxicology, Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 177–192, doi:10.1016/b0-32-301125-x/50024-8, ISBN 978-0-323-01125-9
