This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2011) |
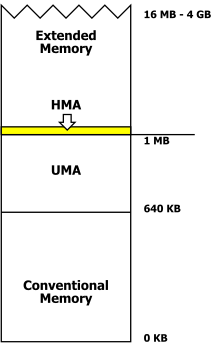
In IBM PC compatible computing, DOS memory management refers to software and techniques employed to give applications access to more than 640 kibibytes (640*1024 bytes) (KiB) of "conventional memory". The 640 KiB limit was specific to the IBM PC and close compatibles; other machines running MS-DOS had different limits, for example the Apricot PC could have up to 768 KiB and the Sirius Victor 9000, 896 KiB. Memory management on the IBM family was made complex by the need to maintain backward compatibility to the original PC design[1] and real-mode DOS, while allowing computer users to take advantage of large amounts of low-cost memory and new generations of processors. Since DOS has given way to Microsoft Windows and other 32-bit operating systems not restricted by the original arbitrary 640 KiB limit of the IBM PC, managing the memory of a personal computer no longer requires the user to manually manipulate internal settings and parameters of the system.
The 640 KiB limit imposed great complexity on hardware and software intended to circumvent it; the physical memory in a machine could be organised as a combination of base or conventional memory (including lower memory), upper memory, high memory (not the same as upper memory), extended memory, and expanded memory, all handled in different ways.