 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Enablex, Emselex |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605039 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 15 to 19% (dose-dependent) |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2D6- and CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 13 to 19 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (60%) and biliary (40%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.382 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
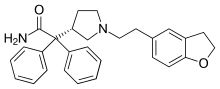
| Formula | C28H30N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 426.560 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Darifenacin (trade name Enablex in United States and Canada, Emselex in the European Union) is a medication used to treat urinary incontinence due to an overactive bladder.[1][2][3] It was discovered by scientists at the Pfizer research site in Sandwich, UK under the identifier UK-88,525 and used to be marketed by Novartis. In 2010, the US rights were sold to Warner Chilcott for US$400 million.
- ^ Croom KF, Keating GM (2004). "Darifenacin: in the treatment of overactive bladder". Drugs & Aging. 21 (13): 885–92, discussion 893–4. doi:10.2165/00002512-200421130-00005. PMID 15493952. S2CID 41549419.
- ^ Parsons M, Robinson D, Cardozo L (July 2005). "Darifenacin in the treatment of overactive bladder". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 59 (7): 831–8. doi:10.1111/j.1368-5031.2005.00585.x. PMID 15963212. S2CID 39061659.
- ^ Chughtai B, Levin R, De E (2008). "Choice of antimuscarinic agents for overactive bladder in the older patient: focus on darifenacin". Clinical Interventions in Aging. 3 (3): 503–9. doi:10.2147/cia.s3414. PMC 2682382. PMID 18982920.