 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cerubidine, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682289 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 26.7 hours (metabolite) |
| Excretion | Bile duct and urinary |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.048 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
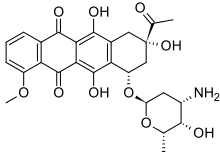
| Formula | C27H29NO10 |
| Molar mass | 527.526 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Daunorubicin, also known as daunomycin, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer.[2] Specifically it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and Kaposi's sarcoma.[2] It is administered by injection into a vein.[2] A liposomal formulation known as liposomal daunorubicin also exists.[2]
Common side effects include hair loss, vomiting, bone marrow suppression, and inflammation of the inside of the mouth.[2] Other severe side effects include heart disease and tissue death at the site of injection.[2] Use in pregnancy may harm the fetus.[2] Daunorubicin is in the anthracycline family of medication.[3] It works in part by blocking the function of topoisomerase II.[2]
Daunorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1979.[2] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[4] It was originally isolated from bacteria of the Streptomyces type.[5]
- ^ "Daunorubicin (Cerubidine) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 19 September 2019. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Daunorubicin hydrochloride". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 8 January 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ British National Formulary: BNF 69 (69th ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. pp. 581–583. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ Lin GQ, You QD, Cheng JF (2011). Chiral Drugs: Chemistry and Biological Action. John Wiley & Sons. p. 120. ISBN 9781118075630. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016.