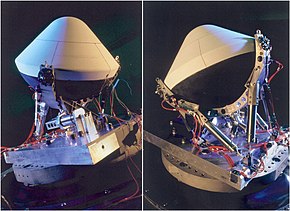
 A Deep Space 2 probe with heatshield and mounting attached to the Mars Polar Lander | |||||||||||
| Mission type | Mars impactor | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator | NASA / JPL | ||||||||||
| Website | jpl.nasa.gov | ||||||||||
| Mission duration | 334 days Mission failure | ||||||||||
| Spacecraft properties | |||||||||||
| Manufacturer | Jet Propulsion Laboratory | ||||||||||
| Launch mass | 2.4 kg (5.3 lb) each | ||||||||||
| Power | 300mW Li-SOCl2 batteries | ||||||||||
| Start of mission | |||||||||||
| Launch date | 20:21:10, January 3, 1999 (UTC) | ||||||||||
| Rocket | Delta II 7425-9.5 D-265 | ||||||||||
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17 | ||||||||||
| Contractor | Boeing | ||||||||||
| Deployed from | Mars Polar Lander (precluded) | ||||||||||
| End of mission | |||||||||||
| Disposal | Failure in transit | ||||||||||
| Last contact | 20:00, December 3, 1999 (UTC)[1] | ||||||||||
| Mars impactor | |||||||||||
| Spacecraft component | Amundsen and Scott | ||||||||||
| Impact date | ~20:15 UTC ERT, December 3, 1999 | ||||||||||
| Impact site | 73°S 210°W / 73°S 210°W (projected) | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
 Mars Surveyor 98 mission logo | |||||||||||
Deep Space 2 was a NASA space probe, part of the New Millennium Program. It included two highly advanced miniature space probes that were sent to Mars aboard the Mars Polar Lander in January 1999.[1] The probes were named "Scott" and "Amundsen", in honor of Robert Falcon Scott and Roald Amundsen, the first explorers to reach the Earth's South Pole. Intended to be the first spacecraft to penetrate below the surface of another planet, after entering the Mars atmosphere DS2 was to detach from the Mars Polar Lander mother ship and plummet to the surface using only an aeroshell impactor, with no parachute. The mission was declared a failure on March 13, 2000, after all attempts to reestablish communications following the descent went unanswered.[2]
The Deep Space 2 development costs were US$28 million.[3]
- ^ a b Davis, Phil; Munsell, Kirk (January 23, 2009). "Missions to Mars: Deep Space 2 - Key Dates". Solar System Exploration. NASA. Archived from the original on April 20, 2009. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
- ^ "Deep Space 2 (DEEPSP2)". NSSDC Master Catalog. NASA - National Space Science Data Center. 2000. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
- ^ "Mars Polar Lander Mission Costs". The Associated Press. 1999-12-08. Retrieved 2020-09-30.