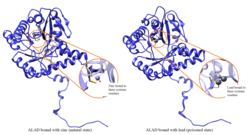
Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (porphobilinogen synthase, or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate dehydratase) is an enzyme (EC 4.2.1.24) that in humans is encoded by the ALAD gene.[5][6] Porphobilinogen synthase (or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate dehydratase) synthesizes porphobilinogen through the asymmetric condensation of two molecules of aminolevulinic acid. All natural tetrapyrroles, including hemes, chlorophylls and vitamin B12, share porphobilinogen as a common precursor. Porphobilinogen synthase is the prototype morpheein.[7]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000148218 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028393 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Eiberg H, Mohr J, Nielsen LS (February 1983). "delta-Aminolevulinatedehydrase: synteny with ABO-AK1-ORM (and assignment to chromosome 9)". Clinical Genetics. 23 (2): 150–4. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb01864.x. PMID 6839527. S2CID 27267679.
- ^ Beaumont C, Foubert C, Grandchamp B, Weil D, Gross MS, Nordmann Y (May 1984). "Assignment of the human gene for delta aminolevulinate dehydrase to chromosome 9 by somatic cell hybridization and specific enzyme immunoassay". Annals of Human Genetics. 48 (2): 153–9. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01010.x. PMID 6378062. S2CID 24098976.
- ^ Jaffe EK, Lawrence SH (March 2012). "Allostery and the dynamic oligomerization of porphobilinogen synthase". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 519 (2): 144–53. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2011.10.010. PMC 3291741. PMID 22037356.