| Deltoid muscle | |
|---|---|
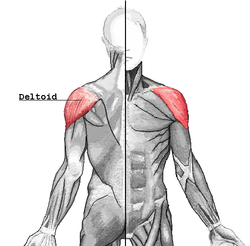 Deltoid muscle | |
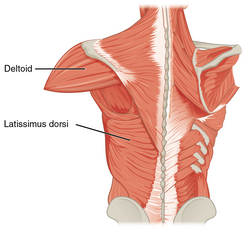 | |
| Details | |
| Origin | The anterior border and upper surface of the lateral third of the clavicle, acromion, spine of the scapula |
| Insertion | Deltoid tuberosity of humerus |
| Artery | Thoracoacromial artery, anterior and posterior humeral circumflex artery |
| Nerve | Axillary nerve |
| Actions | Shoulder abduction, flexion and extension |
| Antagonist | Latissimus dorsi |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus deltoideus |
| MeSH | D057645 |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.002 |
| TA2 | 2452 |
| FMA | 32521 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The deltoid muscle is the muscle[citation needed] forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis)
- posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis)
- intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis)
The deltoid's fibres are Pennate muscle. However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system.[1]
It was previously called the deltoideus (plural deltoidei) and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek capital letter delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further shortened in slang as "delt".
A study of 30 shoulders revealed an average mass of 191.9 grams (6.77 oz) in humans, ranging from 84 grams (3.0 oz) to 366 grams (12.9 oz).[2]
- ^ Brown, JM; Wickham, JB; McAndrew, DJ; Huang, XF (2007). "Muscles within muscles: Coordination of 19 muscle segments within three shoulder muscles during isometric motor tasks". J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 17 (1): 57–73. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2005.10.007. PMID 16458022.
- ^ Potau, JM; Bardina, X; Ciurana, N; Camprubí, D. Pastor JF; de Paz, F. Barbosa M. (2009). "Quantitative Analysis of the Deltoid and Rotator Cuff Muscles in Humans and Great Apes". Int J Primatol. 30 (5): 697–708. doi:10.1007/s10764-009-9368-8. S2CID 634575.
