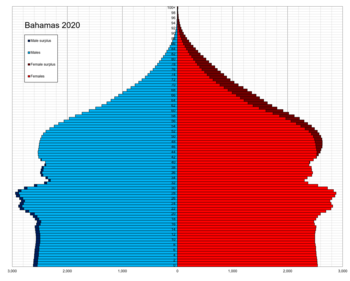
This is a demography of the population of the Bahamas including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1845 | 26,491 | — |
| 1851 | 27,519 | +3.9% |
| 1861 | 35,487 | +29.0% |
| 1871 | 39,162 | +10.4% |
| 1881 | 43,521 | +11.1% |
| 1891 | 47,565 | +9.3% |
| 1901 | 53,735 | +13.0% |
| 1911 | 55,944 | +4.1% |
| 1921 | 53,031 | −5.2% |
| 1931 | 59,828 | +12.8% |
| 1943 | 68,846 | +15.1% |
| 1953 | 84,841 | +23.2% |
| 1963 | 130,220 | +53.5% |
| 1970 | 168,812 | +29.6% |
| 1980 | 209,505 | +24.1% |
| 1990 | 255,049 | +21.7% |
| 2000 | 303,611 | +19.0% |
| 2010 | 351,461 | +15.8% |
| 2022 | 399,314 | +13.6% |
| Source:[1] | ||
Ninety percent of the Bahamian population identifies as being primarily of African ancestry. About two-thirds of the population lives on New Providence Island (the location of Nassau), and about half of the remaining one-third lives on Grand Bahama (the location of Freeport).
The islands were sparsely settled and a haven for pirates until the late 18th century, when thousands of British Loyalists were given compensatory land grants following the American Revolution. Many new settlers were from the Southern United States and brought slaves with them to cultivate plantations. At the turn of the 20th century, the total population was 53,000.
School attendance is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16. There are 158 public schools and 52 private schools in the Bahamas catering to more than 66,000 students. The College of the Bahamas, established in Nassau in 1974, provides programmes leading to associate's degrees and bachelor's degrees; the college is now converting from a two-year to a four-year institution.

- ^ "2000 Round of Population and Housing Census Data Analysis Sub-project: The Bahamas" (PDF). Caricomstats.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 January 2012. Retrieved 30 August 2017.