This article contains several duplicated citations. The reason given is: DuplicateReferences detected: (September 2024)
|
| Demographics of Earth | |
|---|---|
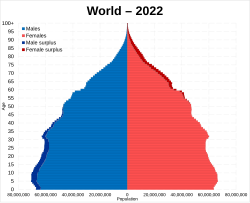 Population pyramid of the world in 2022 by the UN | |
| Population | Over 8,120,531,329 (estimated) |
| Fertility rate | 2.27 (2021) |
Earth has a human population of over 8 billion as of 2024, with an overall population density of 50 people per km2 (130 per sq. mile). Nearly 60% of the world's population lives in Asia, with more than 2.8 billion in the countries of India and China combined. The percentage shares of China, India and rest of South Asia of the world population have remained at similar levels for the last few thousand years of recorded history.[1][2] The world's literacy rate has increased dramatically in the last 40 years, from 66.7% in 1979 to 86.3% today.[3] Lower literacy levels are mostly attributable to poverty.[citation needed] Lower literacy rates are found mostly in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa.[4]
The world's population is predominantly urban and suburban,[5] and there has been significant migration toward cities and urban centres. The urban population jumped from 29% in 1950 to 55.3% in 2018.[6][7] Interpolating from the United Nations prediction that the world will be 51.3 percent urban by 2010, Ron Wimberley, Libby Morris and Gregory Fulkerson estimated 23 May 2007 would have been the first time the urban population was more populous than the rural population in history.[8] India and China are the most populous countries,[9] as the birth rate has consistently dropped in wealthy countries and until recently remained high in poorer countries. Tokyo is the largest urban agglomeration in the world.[7]
As of 2024, the total fertility rate of the world is estimated at 2.25 children per woman,[10] which is slightly below the global average for the replacement fertility rate of approximately 2.33 (as of 2003).[11] However, world population growth is unevenly distributed, with the total fertility rate ranging from the world's lowest of 0.8 in South Korea,[12] to the highest of 6.7 in Niger.[13] The United Nations estimated an annual population increase of 1.14% for the year of 2000.[14] The current world population growth is approximately 1.09%.[7] People under 15 years of age made up over a quarter of the world population (25.18%), and people age 65 and over made up nearly ten percent (9.69%) in 2021.[7]
The world population more than tripled during the 20th century from about 1.65 billion in 1900 to 5.97 billion in 1999.[15][16][17] It reached the 2 billion mark in 1927, the 3 billion mark in 1960, 4 billion in 1974, and 5 billion in 1987.[18] The overall population of the world is approximately 8 billion as of November 2022. Currently, population growth is fastest among low wealth, least developed countries.[19] The UN projects a world population of 9.15 billion in 2050, a 32.7% increase from 6.89 billion in 2010.[15]
- ^ "China's Population 1.4 billion 2020". ABC News.
- ^ "India Population 1.38 billion UN Data Estimate".
- ^ "Literacy rate, adult total (% of people ages 15 and above) | Data". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- ^ "Illiteracy rates by world region 2016". Statista. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- ^ Ritchie, Hannah; Roser, Max (13 June 2018). "Urbanization". Our World in Data.
- ^ "Urban population (% of total population) | Data". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- ^ a b c d CIA.gov World Factbook – World Statistics
- ^ World Population Becomes More Urban That Rural
- ^ "Country Comparison :: Population". U.S. Census Bureau. 2008. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- ^ "World Population Prospects: Data Portal – Population Division". United Nations.
- ^ Espenshade TJ, Guzman JC, Westoff CF (2003). "The surprising global variation in replacement fertility". Population Research and Policy Review. 22 (5/6): 575. doi:10.1023/B:POPU.0000020882.29684.8e. S2CID 10798893., Introduction and Table 1, p. 580
- ^ "Fertility rate, total (births per woman) - Korea, Rep". World Bank.
- ^ "Fertility rate, total (births per woman) - Niger". World Bank.
- ^ "Census.gov". Census.gov. 7 January 2009. Archived from the original on 23 August 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ a b World Population Prospects: The 2008 Revision Population Database Archived 7 April 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The World at". Un.org. 12 October 1999. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ "Population Growth over Human History". Globalchange.umich.edu. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ World Population Milestones
- ^ "United Nations Population Fund". UNFPA. 13 May 1968. Archived from the original on 22 August 2010. Retrieved 6 September 2018.